Blockchain India Policy

WHAT IS BLOCKCHAIN?
A Blockchain is a growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked using cryptography. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. By design, a Blockchain is resistant to modification of the data.
A Database. A list of records/transactions, like a ledger, that keeps growing as more entries are added
Which Is Distributed. Copies of the entire database are stored on multiple computers on a network, syncing within minutes/seconds
Adjustably Transparent. Records stored in the database may be made visible to relevant stakeholders without risk of alteration
Highly Secure. Malicious actors (hackers) can no longer just attack one computer and change any records
And Immutable. The mathematical algorithms make it impossible to change/delete any data once recorded and accepted
POTENTIAL BUSINESS FEATURES OF BLOCKCHAIN

Improving profitability and quality
Automation using smart contracts/algorithms
Traceability of all historical transactions
Speed and efficiency of transactions by eliminating intermediaries
Enhanced security by encryption of data at the stage of dissemination
Prevents tampering as any tampering may leave behind a trail
Increasing transparency
Distributed ledger
Provides a comprehensive picture: all stakeholders see the same information to which they have access
Availability of multiple copies of the shared data
Reinventing products and processes
Transparent and predefined rules which facilitate the creation of new products/processes through a decentralized model
Tokenization / Digital Assets which are physical objects with a unique digital representation that enables digital ownership, management and transfer
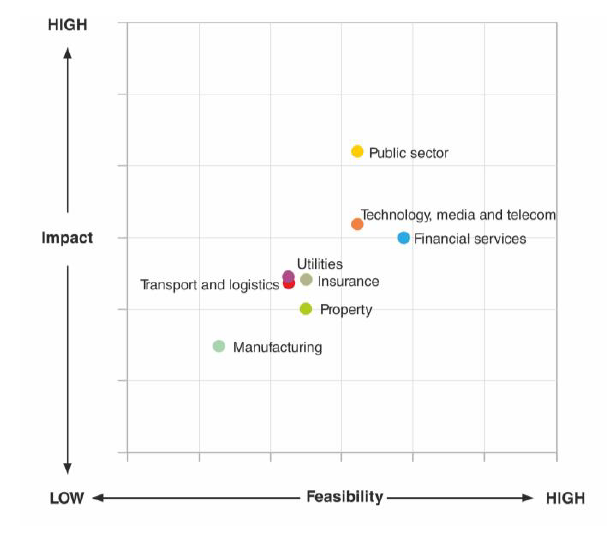
Economic Potential of blockchain by industry sectors
India’s Digital Foundational Infrastructure

Aadhaar
World’s largest identity database with more than 1.2bn biometric identities
More than 25 million authentications per day
Unified Payments Interface (UPI)
World’s most sophisticated digital payments system
1.3bn transactions processed in December 2019
Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN)
More than 400 million returns filed
More than 800 million invoices uploaded
PM-JAY
World’s largest healthcare initiative with
~500 million beneficiaries covered ~119 million e-cards issued so far,
BLOCKCHAIN POSSIBILITIES IN E-GOVERNANCE
-
Land Records: Creating a new system to manage land record transfer and ownership
-
Securing Government issued certificates and documents
-
Pharmaceutical drugs supply chain through blockchain enabled trust
-
Blockchain solution for educational certificates
-
Immunization Supply Chain
-
A blockchain based model for subsidies and benefit transfers
-
Tracking and Provence of Organic Farming
-
Securing energy trading through Blockchain
-
Secure payments and transactions in immutable records
Various government services transactions can be stored in blockchain for immutable records that cannot be tampered with. This avoids duplications and malpractices.
Land Registry
Stamp duty paid
Registration
Payments
Land transfer records
Pharmaceutical
Formulation records
Formulation Manufacturer
Distributor
Transportation monitored under specific conditions
Pharmacy
Education Sector
E-Certificates
School Certification
College and Institution certificates
Students Access info
Identity Verification
Agriculture
Production and Traceability
Organic Certification
Storage records
Transportation and supply chain
Subsidies given to farmers
Summary
Governance in India faces unique challenges given the scale, diversity and complexity of processes involved for delivery of varied public services. Blockchain offers unique possibilities of addressing issues relating to improving governance. In business, by allowing ‘self-regulation’, India can considerably move towards improving the ‘Ease of Doing Business’ by allowing entities to interact through a trusted medium with a reduced dependency on cumbersome regulatory oversight and compliance. By empowering citizens through features of transparency, decentralization and accountability, blockchain would help in improving ease of living.
To know more about blockchain and build your next blockchain based solution you can reach us at contact@smartchainers.com or our website
Read More Blogs
The Blockchain Necessity Framework
Blockchain has been positioned as a revolutionary new technology...
Learn MoreDigital Wallet and Cryptocurrencies
Blockchain is one of the greatest innovation in the modern world for...
Learn More
